Numeric Banding: Summary View
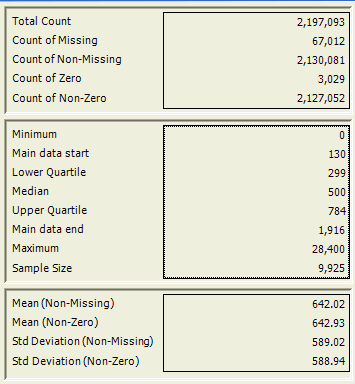
Count Statistics
The top panel gives a summary of the volumes of data analysed during the banding process. All the count statistics are based on records at the resolve level of the variable being banded with the base selection applied.
|
Total Count |
The number of all records at the resolve level of the variable being banded, irrespective of the variable value. For example, the number of holidays when banding the cost variable. |
|
Count of Missing |
The number of records where the variable being banded has a missing value.
|
|
Count of Non-Missing |
The Total Count minus the Count of Missing. This is the number of records which could be allocated to a range (if the set of ranges span the complete set of values for the variable). This count is used when calculating the mean and standard deviation of non-missing values.
|
|
Count of Zero |
The number of records where the variable being banded has a value of exactly zero.
|
|
Count of Non-Zero |
The Total Count minus the Count of Zero. This count is used when calculating the mean and standard deviation of non-zero values.
|
Value Statistics
The middle panel gives a summary of the individual values held by the variable. The value statistics are only based on records within the base selection. For example, the Minimum and Maximum report the smallest and largest value observed within the selection, rather that across all the data.
|
The lowest value within the base selection |
|
|
Main Data Start |
The value at which the main bulk of the data begins (the 2.5%ile) within the base selection. Values below this value are considered extreme and will be allocated to an extended range at the start of the distribution of the default options are used.. If the distribution has a few extremely low values, the Main Data Start will be considerably higher than the Minimum value.
|
|
Lower Quartile |
The value below which 25% of the values of this variable fall within the base selection |
|
Median |
The value above and below which 50% of the values of this variable fall within the base selection. This is the middle value if all values were arranged in order. |
|
Lower Quartile |
The value above which 25% of the values of this variable fall within the base selection. |
|
Main Data End |
The value at which the main bulk of the data stops (the 97.5%ile) within the base selection. Values above this value are considered extreme and will be allocated to an extended range at the end of the distribution of the default options are used. If the distribution has a few extremely high values, the Main Data End will be considerably lower than the Maximum value.
|
|
Maximum |
The highest value within the base selection |
|
Sample Size |
A sample is used to determine all value statistics (apart from the minimum and maximum). This is because these statistics require data values to be ordered and the sorting process can be slow if all records are used. By default a sample of roughly 10,000 records is used (providing that there are sufficient populated records in the base selection.) To produce a set of Quantile Ranges the full data is processed and so the value statistics will be updated based on this full sample. Values may change slightly as a result.
|
Distribution Moment Statistics
The lower panel gives a summary of the distribution moments for this variable for the records within the base selection. For example, the Mean reports the average value within the selection, rather that across all the data.
|
Mean (Non-Missing) |
The average of all the populated values for this variable within the base selection. This is calculated as the sum of all the values divided by the Count of Non-Missing.
|
|
Mean (Non-Zero) |
The average of all the values which are not zero, for this variable within the base selection. This is calculated as the sum of all the values divided by the Count of Non-Zero.
|
|
Standard Deviation (Non-Missing) |
The standard deviation of all the populated values for this variable within the base selection. This is calculated based on the Count of Non-Missing.
|
|
Standard Deviation (Non-Zero) |
The standard deviation of all the values which are not zero, for this variable within the base selection. This is calculated based on the Count of Non-Zero.
|