Simple Customer Journey Analysis
Event-driven, point-in-time behavioural modelling allows you to take simple transactional selections and generate a model around a particular sequence of events, centred on a particular point in time. Defining and analysing customer journeys allows you to learn from customer behaviour in the past in order to predict customer behaviour in the future.
Scenario
In this example, let's consider that the objective of our analysis is to understand which people first book a holiday to Australia and then go on to book a travel insurance policy. Modelling will be carried out on:
-
a Base selection - people who booked a holiday to Australia
and then understanding the differences between this group and
-
an Analysis selection - people who booked a holiday to Australia AND also purchased a travel insurance policy
The Base and Analysis selections are dynamically generated by FastStats after you create and drag simple Event selections into the Modelling Environment.
Note:
1. Event selections must be from a table level which is a direct child of the modelling level chosen
.png)
2. Event selections are usually very simple criteria that specify the relevant type of transactional activity
3. Event selections should not include any date criteria
Here the modelling level is Person and, in the Holidays system, you might then choose Event selections created at the Bookings or Policies level - e.g. Bookings to Australia and travel Insurance Policyof any kind.
-
Create the selections shown below
.png)
-
Drag these selections onto the Selections tab window in the Modelling Environment
FastStats automatically classifies the selections as Type - Event and, because both selections have been created on tables immediately below the Person table level, their Validation Status is Valid.
Creating the event driven Base selection
The Base selection for use in event driven must now be dynamically created by FastStats using the Event selection that relates to what people should have done in order to be in the Base selection - here:
-
Right click on the Bookings to Australia selection and select Create simple event-driven Base selection
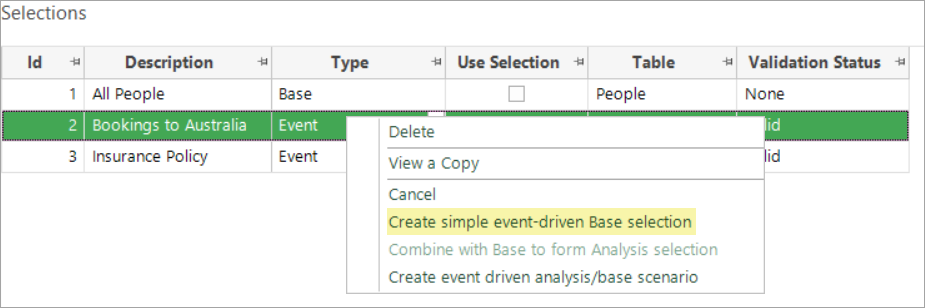
The Training Date of 20/10/2019 defined earlier broadly specifies which historical data we are analysing, and the dialog that now appears allows you to specify the time frame in which the base event should occur relative to this.
-
Select Booking Date and use the drop down options to define a period of 3 Months Before Training Date and OK
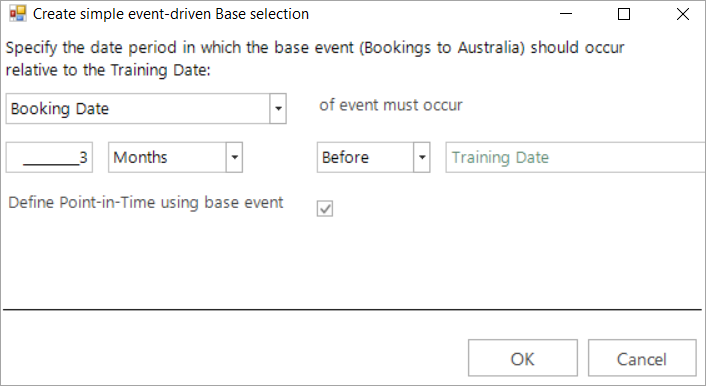
A dynamic Base selection is added to the Modelling Environment and these settings determine that people who have booked a holiday in the 3 months before the Training Date are selected.
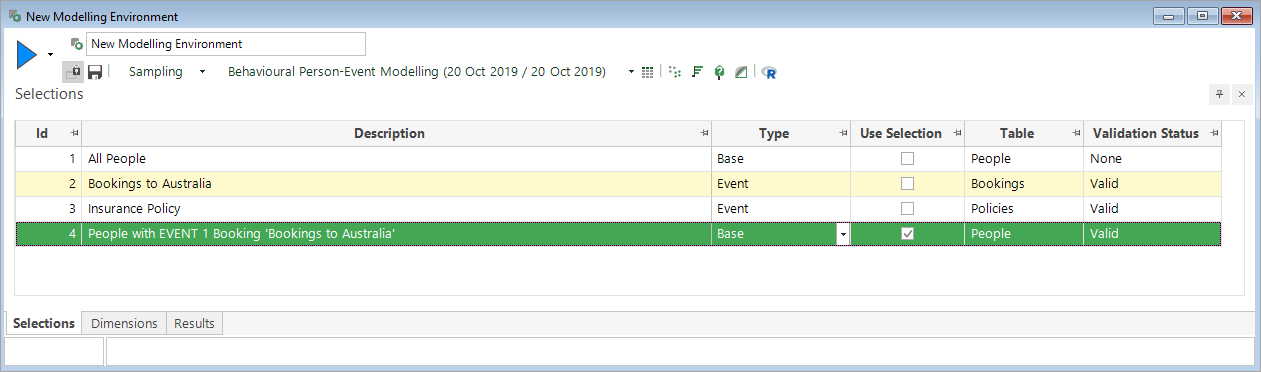
To see the selection criteria, you can right click on the Base selection and select to View a Copy:
.png)
Notice that the selection is at the People level - determined by the modelling level set earlier. The criteria from the Event selection are now combined with a DateDiff Expression to find people with a booking that matches the base event criteria up to 3 months before "Today" - the value of Today being set to either the Training Date or the Evaluation Date.
.png)
Creating the event driven Analysis selection
The Analysis selection for use in event driven must now be dynamically created by FastStats using the Event selection that relates to what people should have done in order to be in the Analysis selection - over and above the base event - here this is people who booked to Australia but then went on to purchase a travel insurance policy.
-
Right click on the Insurance Policy selection and select Combine with Base to create Analysis selection
Note: This option is inaccessible if you have not already created a Base selection.
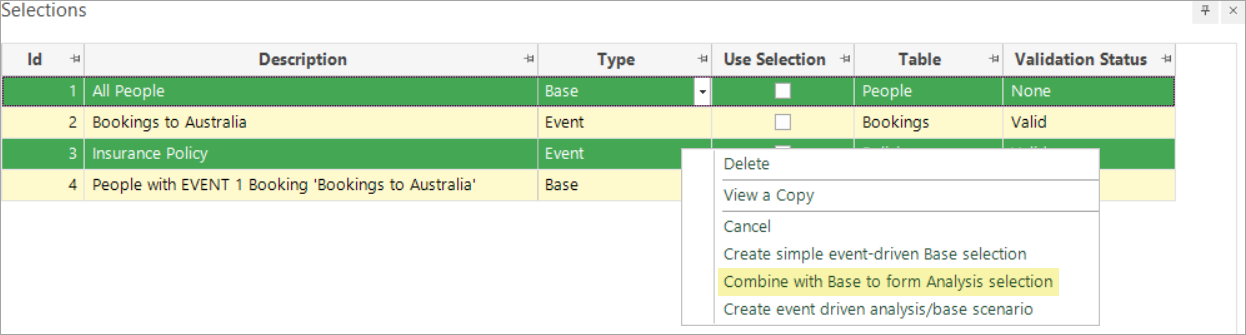
The dialog that opens is where you determine the time frame within which the analysis event should occur, relative to the point in time set within the base event.
-
Complete the settings as in the screenshot below:
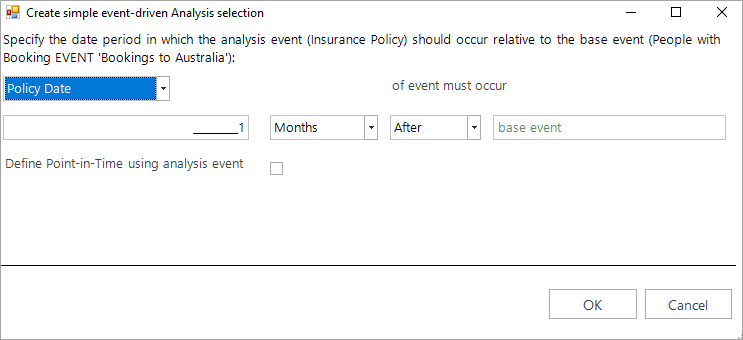
In this example, the insurance policy must have been taken out up to one month after the base event. As the intention is to try and predict this future event, the analysis event is after the base event. You can view a copy of the selection criteria:
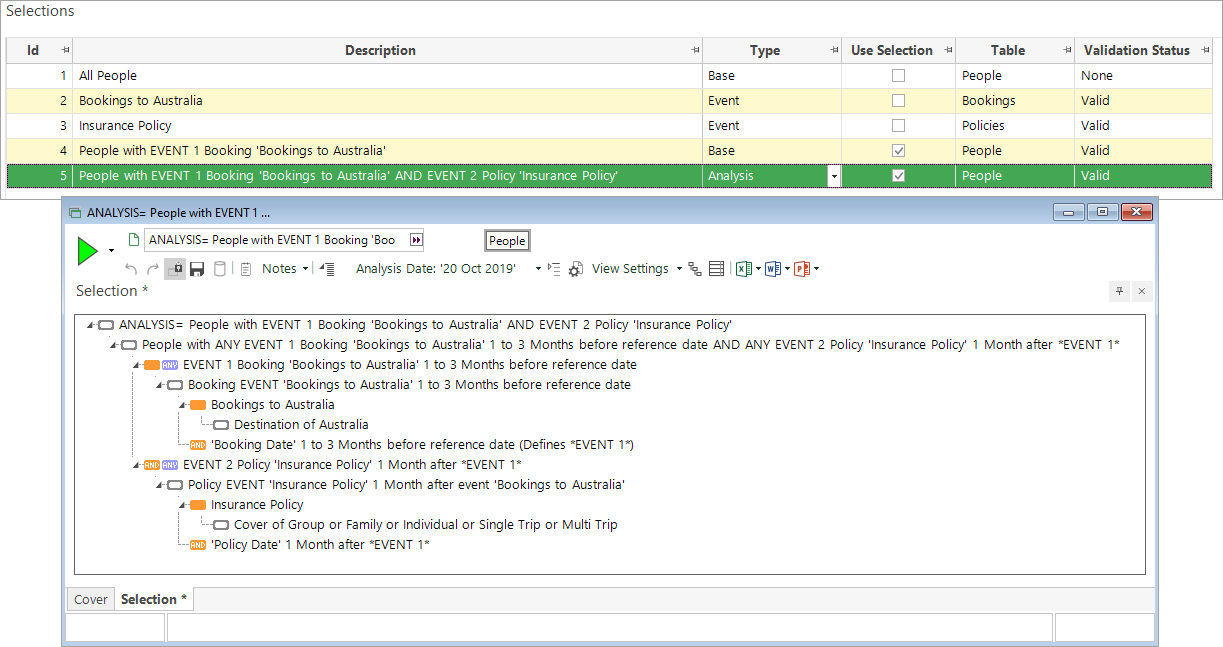
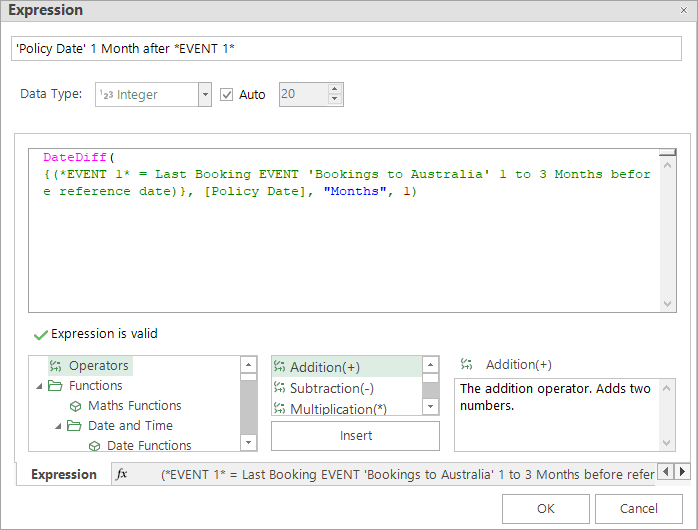
Again - by editing the Policy Date criteria, you can see that a DateDiff Expression has been used to relate the Policy Date to the point in time defined.
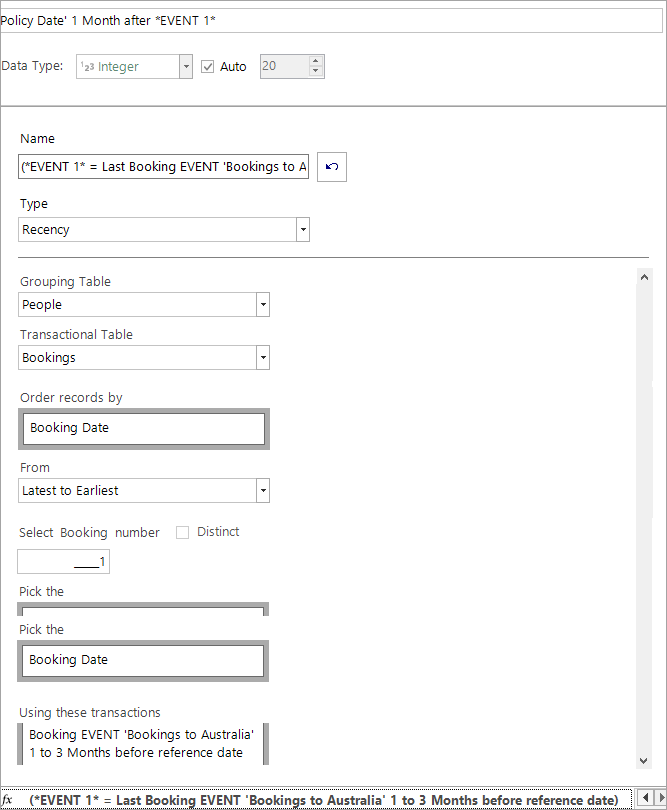
Definition of the "Point-in-Time"
The Point-in-Time refers to the date of the base event booking. This is used to specify when the analysis event must occur, and will also be used in modelling when creating features such as “count of bookings before the point in time”.
Note:
Where multiple base events have occurred within the time frame, it is the date of the event closest to the Training Date which determines the point-in-time. The Point-in-Time is a recency aggregation selecting the closest base event to the Training Date:
Once you have completed this set-up, you can explore different behavioural features on the Dimensions tab and create a PWE model. The behavioural features will all reference date periods that are relative to the Point-in-Time.
Related topics:
-
Modelling Environment: How do I create a Behaviour-based Model?
-
Modelling Environment: Behaviour-based Modelling - Transactional Combinations